Belt Feeders Manufacturer
Belt Feeder
UHM offers heavy-duty belt feeders that are capable of handling nearly any material.
Belt feeders can be applied to withdraw fines or wet materials under hoppers, bins or stock piles to provide the desired, continuous feed rate for screens, crushers, and conveyors.
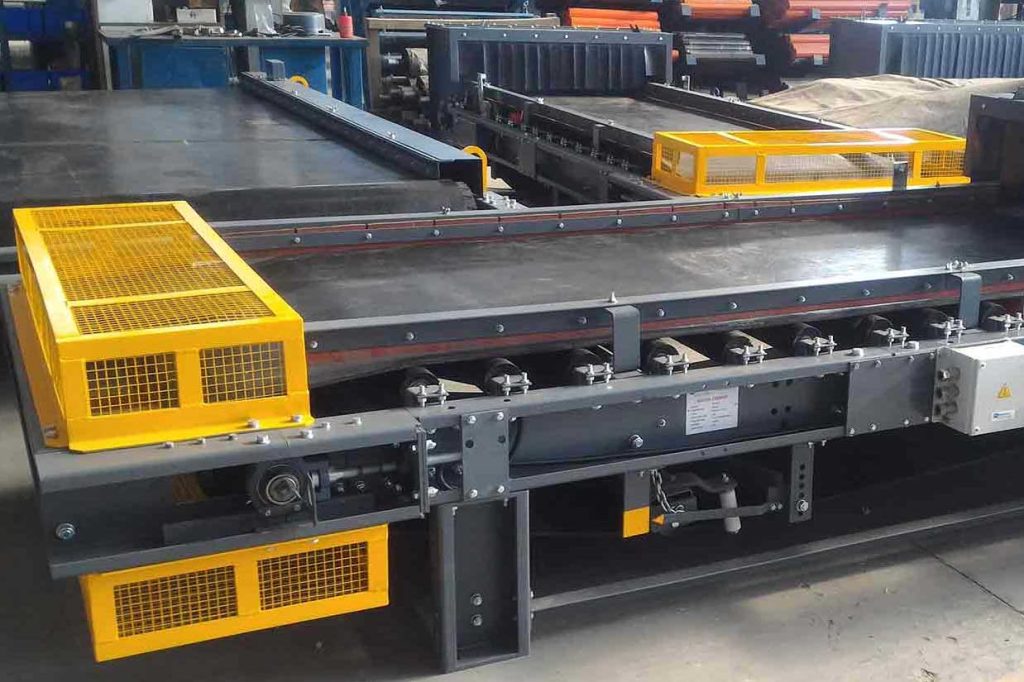

Belt feeders
Easy to operate and adapt, UHN's Belt Feeders control moving feed from the mine truck into the plant by extracting smaller particle sizes, grains, or materials from hoppers, bins, silos, and stockpiles.
Belt feeders can be applied to withdraw fines or wet materials under hoppers, bins or stock piles to provide the desired, continuous feed rate for screens, crushers, and conveyors. Belt feeders are commonly used when material that is either stockpiled or loaded (at an uncontrolled rate) in a bin or hopper needs to be introduced into the system at a controlled feed rate. Able to handle a variety of materials, belt feeders are reliable and useful in an endless amount of applications.
Belt feeders’ technical specifications
- Belt width: From 24” up to 72”
- Maximum capacity: 2628 t/h
- Maximum speed: 0.3 m/s
- Maximum lump size: 267 mm (10 1/2”)
- Belt feeder slope: Horizontal
- Feeding direction: One way
Read More: Bulk Material Feeder: Basics, 3 Types & Operating Principles
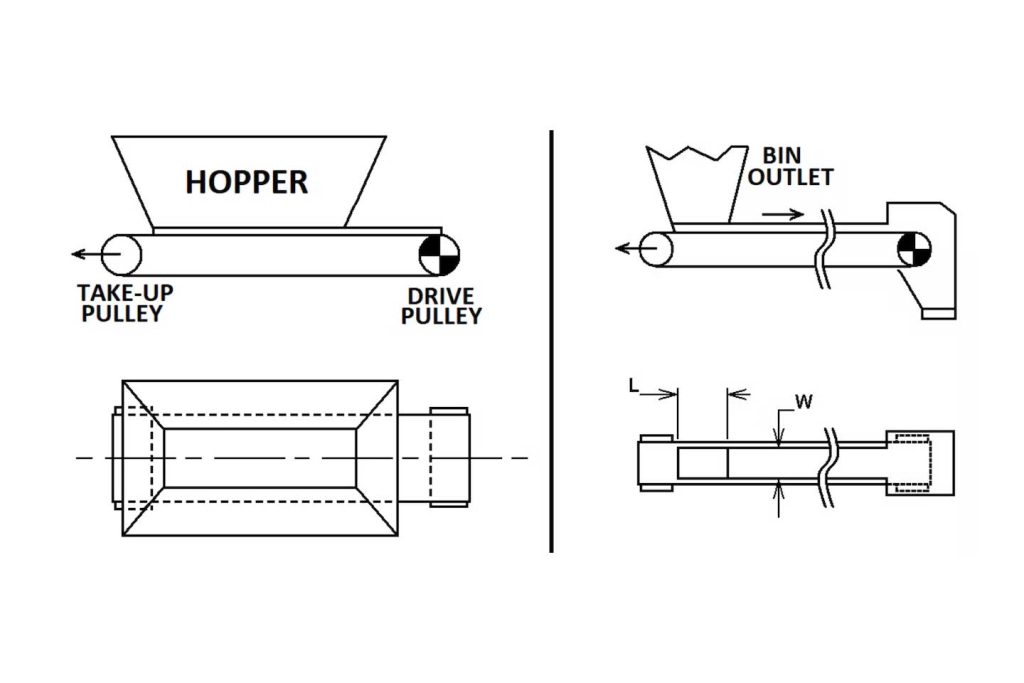
Works Principle of Belt Feeders
A belt feeder consists of a hopper positioned directly over a belt conveyor. The belt conveyor “pulls” material out from under the hopper, while an adjustable vertical strike-off plate controls the height of material allowed to advance as the belt moves forward, or in other words, the material profile on the belt. Skirt boards contain material on the belt.
Belt feeders operate at much slower speeds compared to regular troughed belt conveyors – typically in the range of 30-60 FPM and usually not exceeding 100 FPM.
Structure
Belt feeders are similar to belt conveyors in terms of their componentry and design. They consist of pulleys (typically two), a drive unit, a take-up unit, idlers, and a belt. Belt feeders are usually configured horizontally and are most commonly used to empty (drawdown) material from within a bin or hopper. The bulk material is progressively removed from the bin or hopper through shear forces applied to the material by the belt.
Works Cited: Bulk material feeder types and applications;
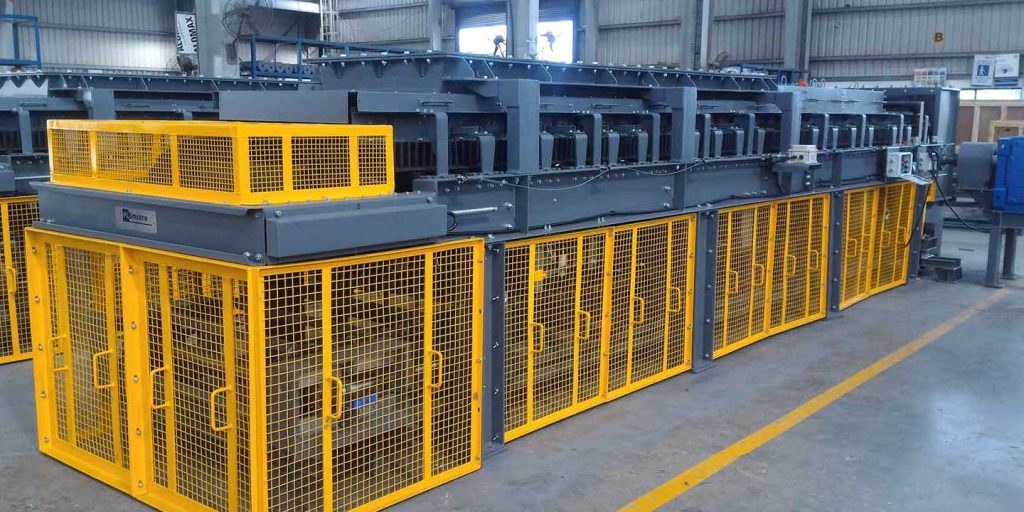

Two Control Methods of Belt Feeders
Belt feeders are run at low belt speeds (relative to belt conveyor belt speeds), typically in the range of 0.25 to 0.5 m/s. Accordingly, they utilize much wider belting than a belt conveyor carrying the same capacity (tph). Belt feeders cannot run at higher speeds because they impart considerable force on the material to remove it from the bin or hopper. The slower speed also ensures more accurate material flow control.
Another control method for the flow of material on a belt feeder is the use of a profile plate or shear bar, which is essentially a volumetric capacity control. This is a steel plate or bar placed above the belt line just outside the leading edge of the discharge from the bin or hopper. The height is calculated based on the required cross-sectional area of material to be transported on the feeder.
Applications of Belt Feeders
Belt feeders are typically inserted into a system at the loading point of a belt conveyor. They are available in a wide range of ratings from light to super-heavy duty. Accordingly, they appear in many industries. Super-heavy-duty belt feeders are most commonly used in applications such as mines handling large, heavy rocks, whereas light-duty belt feeders are often used in manufacturing or even food or pharmaceutical applications.
The precise control belt feeders lend to bulk solids handling makes them useful in a diverse range of applications. Capable of handling everything from sand to ore, belt feeders are especially critical when working with bulk solids that exhibit poor flowability. They are often found in the following settings:
- Pulp and paper mills
- Power generation plants
- Mining and mineral processing operations
- Fertilizer production and blending plants
- Chemical production facilities
- Aggregate handling operations
Top 4 Benefits of UHM Belt Feeders
Benefit 1#: Versatile applications
Developed according to strict safety standards and for easy maintenance, transport, and installation, belt feeders are widely used in mining operations, power generation and construction applications, as well as pulp and paper plants, fertilizer plants, and in grain industry or anywhere bulk materials handling is required.
Benefit 2#: Optimization options
Available in standard capacity and high capacity models models, belt feeders can be implemented in fixed circuits or fitted with wheels for easy transportation. We also offer a wide range of additional features and services for these feeders to enable maximum efficiency of your operations.
Benefit 3#: Safe to operate
Belt feeders are built according to strict safety standards, such as NRs (Brazilian regulations) and OSHA and MSHA (United States regulations). They include an emergency stop as well as misalignment and under speed switches to ensure operator safety. Optional features can also be fitted to additionally improve overall safety.
Benefit 4#: Simplified maintenance
The rugged design and features such as an abrasion resistant liner help significantly increase service life. Additionally, components are easy to access, which simplifies the maintenance process so spare and wear parts can be quickly and easily replaced with minimal downtime.